Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders affect millions of people worldwide, causing discomfort, pain, and difficulty with basic functions like chewing and speaking. Advances in medical and dental technologies have revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment of TMJ disorders, providing patients with more effective and less invasive options. In 2025, new innovations promise to make managing TMJ disorders even more efficient and personalized, with breakthroughs in dental software and other cutting-edge tools taking center stage.
The Evolving Landscape of TMJ Treatment
Traditionally, TMJ disorders were managed using a combination of physical therapy, medication, oral appliances, and, in severe cases, surgery. However, these treatments often relied heavily on trial and error, as precise diagnosis and individualized treatment plans were challenging. Recent advancements in dental software and imaging technologies are changing this narrative, enabling clinicians to pinpoint the root cause of TMJ disorders and develop tailored interventions with unprecedented accuracy.
Innovative Diagnostic Tools
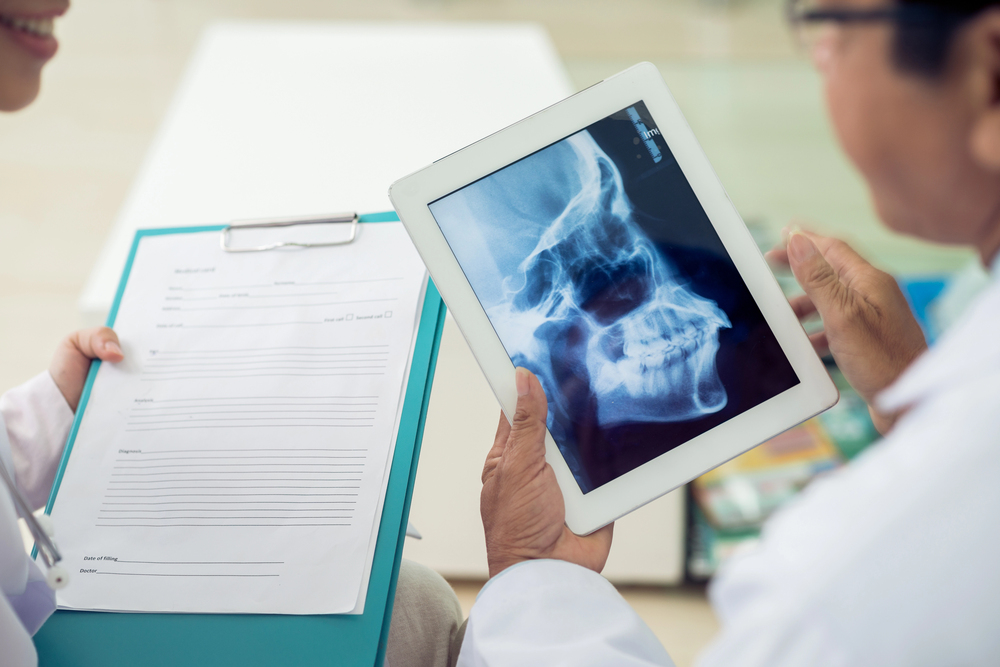
One of the most significant developments in 2025 is the use of 3D imaging technologies. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans are now more accessible and detailed, providing high-resolution images of the temporomandibular joint. These scans allow dental professionals to visualize the joint’s structure, detect abnormalities, and assess the extent of damage with precision.
Paired with advanced dental software, CBCT scans can now be integrated into virtual treatment planning systems. These systems create comprehensive models of a patient’s jaw and surrounding structures, allowing for a thorough analysis of how the TMJ interacts with other components of the oral cavity. This level of detail ensures that clinicians can identify the exact cause of pain, whether it’s joint degeneration, misalignment, or muscle tension.
AI-Powered Dental Software
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in TMJ diagnosis and treatment. AI-powered dental software analyzes patient data—including imaging, medical history, and symptoms—to provide real-time insights and recommendations. These tools can identify patterns that may not be immediately apparent to human clinicians, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
For example, AI algorithms can detect subtle changes in joint movement and alignment from CBCT scans or even track how TMJ symptoms evolve over time. This enables dentists to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans dynamically. Additionally, AI is being integrated into wearable devices that patients can use at home to track jaw movements and muscle activity, creating a continuous feedback loop between patients and their care providers.
Personalized Oral Appliances
Oral appliances remain a cornerstone of TMJ treatment, but new technologies are making them more effective than ever. In 2025, custom oral appliances are being designed with the help of 3D printing and advanced dental software. These tools enable the creation of appliances that are perfectly tailored to a patient’s unique anatomy, ensuring optimal comfort and effectiveness.
Moreover, some appliances now come equipped with embedded sensors that collect data on jaw movement and pressure while in use. This information is transmitted to dental software, allowing clinicians to assess how well the appliance is working and make adjustments as needed. Patients benefit from a more personalized approach that maximizes relief and minimizes discomfort.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
While surgical interventions are sometimes necessary for severe TMJ disorders, advancements in technology are making these procedures less invasive and more precise. Robotic-assisted surgeries are becoming more common, allowing for greater accuracy and reduced recovery times. Additionally, regenerative medicine techniques, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections and stem cell therapies, are gaining traction as viable options for repairing damaged joint tissues.
These minimally invasive treatments are often guided by dental software that maps out the procedure in advance, ensuring that every step is carefully planned and executed. This reduces the risk of complications and improves outcomes for patients.
The Role of Telehealth
Telehealth has become an integral part of TMJ care in 2025, thanks to advancements in digital communication platforms and wearable devices. Patients can now consult with specialists remotely, sharing data from their wearable sensors and dental software directly with their providers. This eliminates the need for frequent in-person visits while maintaining high-quality care.
For instance, patients with TMJ disorders can use mobile apps to report symptoms, track progress, and receive personalized exercises or recommendations. Dental professionals can analyze this data through their software systems and provide tailored advice or adjustments to treatment plans without requiring the patient to visit the clinic.
Future Directions
As technology continues to evolve, the future of TMJ treatment looks promising. Researchers are exploring the potential of virtual reality (VR) for pain management, offering immersive environments that help patients reduce stress and relax their jaw muscles. Additionally, advancements in genomics may lead to personalized medicine approaches, where treatments are tailored based on a patient’s genetic profile.
AI and dental software will likely become even more sophisticated, integrating seamlessly with wearable devices and imaging tools to provide a holistic view of TMJ health. These technologies will empower both patients and clinicians, fostering a more collaborative approach to care.
The advancements in TMJ treatment technologies in 2025 are transforming how dental professionals diagnose and manage this complex condition. From AI-powered dental software to custom oral appliances and minimally invasive procedures, these innovations are providing patients with more effective and personalized solutions. As the field continues to grow, individuals suffering from TMJ disorders can look forward to improved outcomes and a better quality of life.