
Australia Improves Its Dental Cosmetic Procedure Guidelines to Better Protect Patients
Australia has recently updated its guidelines for dental cosmetic procedures, placing a stronger emphasis on patient safety, ethics, and the quality of care provided. This change is a crucial step forward in protecting patients from substandard procedures and ensuring that only qualified practitioners perform these treatments. At the forefront of this effort is Dr. Thea Pabustan, a prominent figure in the Australian dental community, advocating for better patient care and raising awareness about the significance of these new regulations.
The Growing Demand for Cosmetic Dentistry
Cosmetic dentistry has become increasingly popular in Australia over the past decade, with patients seeking procedures to enhance the appearance of their teeth, gums, and overall smile. Treatments such as teeth whitening, veneers, dental implants, and orthodontic work have seen a sharp rise in demand. This surge in interest can be attributed to the growing influence of social media, where picture-perfect smiles are often glorified, and the increased accessibility of cosmetic treatments.
However, this growing demand has also led to an influx of unqualified practitioners offering cosmetic dental services without the necessary skills or training. As a result, many patients have faced adverse outcomes, from botched procedures to long-term damage. Recognizing this problem, Australia has taken steps to strengthen its guidelines around cosmetic dentistry to ensure that patients are better protected and receive safe, quality care.
New Guidelines Focused on Patient Safety
The updated guidelines introduced by the Australian Dental Association (ADA) and the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) place a greater focus on patient safety, informed consent, and the qualifications of dental practitioners performing cosmetic procedures. These guidelines aim to curb the risks associated with unregulated cosmetic treatments by ensuring that only dentists with appropriate qualifications and experience are allowed to carry out such procedures.
One of the significant changes in the updated guidelines is the requirement for practitioners to provide comprehensive information to patients before any cosmetic treatment begins. Patients must be fully informed of the risks, benefits, alternatives, and expected outcomes of the procedures. This step ensures that patients can make well-informed decisions and helps prevent unrealistic expectations from driving the demand for certain treatments.
Additionally, the guidelines call for thorough pre-procedural assessments to evaluate a patient’s dental health, medical history, and suitability for cosmetic treatments. This holistic approach aims to minimize complications and ensures that patients receive treatments that are not only safe but also appropriate for their specific conditions.
Championing Patient Safety
Dr. Thea Pabustan has been a vocal advocate for the new guidelines and has played a critical role in raising awareness about the importance of patient protection in cosmetic dentistry. With years of experience in both general and cosmetic dentistry, Dr. Thea Pabustan has witnessed firsthand the consequences of poorly performed procedures and the distress they can cause patients.
“Cosmetic dentistry is not just about enhancing smiles; it’s about doing it safely and ethically,” says Dr. Pabustan. “Patients deserve to be treated by qualified professionals who prioritize their health and well-being, not just the aesthetics.”
Dr. Pabustan’s advocacy goes beyond promoting safe cosmetic treatments; she has also emphasized the role of early childhood dental care in laying the foundation for long-term oral health. She believes that education on dental hygiene and preventative care from a young age can help reduce the need for extensive cosmetic procedures later in life.
The Role of Early Childhood Dental Care
While cosmetic dentistry often focuses on adults seeking to improve their appearance, the foundation for healthy teeth begins in childhood. Early childhood dental care is crucial in preventing oral health issues that may later necessitate cosmetic procedures. Children who receive proper dental care early on are less likely to develop issues such as cavities, misaligned teeth, and gum disease, all of which can require corrective treatment later.
Dr. Thea Pabustan has highlighted the importance of instilling good oral hygiene habits from a young age and ensuring that children receive regular dental check-ups. “Early childhood dental care isn’t just about preventing cavities—it’s about setting up children for a lifetime of healthy, beautiful smiles,” she explains. “By teaching children and parents the importance of dental hygiene, we can reduce the likelihood of needing more invasive treatments down the road.”
The new guidelines support this approach by emphasizing the importance of preventive care and encouraging parents to take their children for dental visits early and regularly. In fact, the ADA recommends that children have their first dental visit by the time they turn one or when their first tooth appears. Early intervention can address potential issues before they become serious, reducing the need for cosmetic procedures later in life.
A Holistic Approach to Dental Health
The updated cosmetic dentistry guidelines reflect a broader trend in the healthcare industry toward a more holistic approach to patient care. Rather than treating cosmetic procedures as isolated services, dental professionals are encouraged to consider the overall health of the patient, including their mental and emotional well-being. This shift ensures that cosmetic treatments are not only safe but also aligned with the patient’s long-term health goals.
The guidelines also place a significant emphasis on ethics. Practitioners are reminded that while patients may seek drastic cosmetic changes, it is the dentist’s responsibility to recommend treatments that prioritize function and health over aesthetics alone. This ethical approach prevents overtreatment and helps avoid unnecessary procedures that may compromise a patient’s dental health in the long term.
A Step Forward for Patient Protection
Australia’s updated guidelines for dental cosmetic procedures mark a significant step forward in improving patient safety and the quality of care in cosmetic dentistry. By enforcing stricter standards for qualifications, informed consent, and pre-procedural assessments, the guidelines aim to protect patients from harm and ensure that cosmetic treatments are performed by qualified professionals.
Dr. Thea Pabustan has been at the forefront of advocating for these changes, emphasizing the importance of both patient safety and early childhood dental care. As the new guidelines take effect, patients can feel more confident that their dental cosmetic procedures will be safe, ethical, and tailored to their overall well-being, ensuring a healthier future for smiles across Australia.
Understanding the Complexities of an Eating Disorder on Orthodontics
Orthodontics plays a critical role in achieving optimal oral health. It’s not just about straightening teeth or creating a beautiful smile; orthodontic treatments are integral to improving functionality, bite alignment, and overall dental hygiene. However, for individuals with eating disorders, orthodontic treatment presents a unique set of challenges. Eating disorders, such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia, and binge eating disorder, have significant effects on a person’s overall health, including their oral health. For orthodontic patients, the impact of these disorders can complicate treatment and make achieving optimal oral health more difficult.
In this article, we’ll explore the complexities of managing orthodontics in patients with eating disorders, focusing on how these conditions affect dental structures, oral hygiene, and the long-term success of orthodontic treatment.
1. The Link Between Eating Disorders and Oral Health
Eating disorders can have devastating effects on oral health. When considering orthodontics, it’s important to understand how these disorders directly impact the structures involved in treatment and overall oral hygiene.
– Enamel Erosion: One of the most immediate consequences of eating disorders, especially bulimia, is enamel erosion. Frequent vomiting exposes teeth to stomach acids, which erode the protective enamel layer. This erosion weakens the teeth and makes them more susceptible to decay. For orthodontic patients, maintaining healthy enamel is crucial as weakened teeth may struggle to support orthodontic appliances like braces or aligners.
– Cavities and Tooth Decay: Disordered eating often involves poor nutritional intake, which can lead to a lack of essential nutrients needed to maintain strong teeth and gums. A deficiency in vitamins and minerals, such as calcium and vitamin D, can compromise tooth and bone strength, making orthodontic treatments less effective and more prone to complications. Additionally, individuals with eating disorders may neglect oral hygiene practices, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
– Gum Disease: Individuals with eating disorders are at a higher risk of developing gum disease, particularly when poor oral hygiene is combined with malnutrition. Gum disease can make it difficult to properly adjust orthodontic devices, as healthy gums are essential for maintaining the stability of the teeth.
Understanding these factors is crucial for orthodontists when designing a treatment plan. If an eating disorder is present, orthodontists need to be vigilant in identifying and addressing these underlying issues to ensure the success of the treatment and the maintenance of optimal oral health.
2. The Impact of Orthodontic Appliances on Oral Health in Eating Disorder Patients
Orthodontic appliances such as braces, aligners, and retainers require strict oral hygiene practices to prevent complications. However, patients with eating disorders face unique challenges in maintaining this level of hygiene.
– Plaque Accumulation: Orthodontic appliances can make it more difficult to clean the teeth effectively, especially for individuals who are already struggling with poor nutrition or disordered eating behaviors. Plaque can easily build up around brackets and wires, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease. For patients with eating disorders, who may already have compromised oral health due to malnutrition or acidic exposure, the risk is even higher.
– Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): Another common issue among individuals with eating disorders is bruxism, or teeth grinding, which can occur as a result of stress or anxiety. This habit can exacerbate orthodontic problems by putting excessive pressure on teeth and orthodontic appliances. The added stress can result in tooth fractures, enamel wear, or damage to braces, all of which can complicate treatment.
– Difficulty in Wearing Aligners: Patients undergoing orthodontic treatment with clear aligners, such as Invisalign, need to wear the devices for a certain number of hours each day to achieve effective results. However, individuals with eating disorders, particularly those with binge eating disorder, may find it difficult to follow these guidelines. Episodes of binge eating or purging may interfere with the consistent use of the aligners, delaying or compromising the success of the treatment.
To mitigate these issues, orthodontists must take a proactive approach in educating patients about the importance of oral hygiene and ensuring that they are aware of the consequences of neglecting their dental health. Orthodontists should work closely with the patient’s general dentist, nutritionist, or mental health professional to create a comprehensive care plan that addresses both their orthodontic needs and their eating disorder.
3. Strategies for Managing Orthodontic Care in Patients with Eating Disorders
Orthodontists can employ several strategies to ensure optimal oral health in patients with eating disorders. These strategies often require collaboration with a multidisciplinary team, including dental professionals, nutritionists, and mental health practitioners, to address both the dental and psychological aspects of the disorder.
– Early Detection and Intervention: Early identification of signs of an eating disorder is essential in preventing severe oral health complications. Orthodontists should be trained to recognize warning signs, such as enamel erosion or receding gums, which may indicate the presence of disordered eating behaviors. Once identified, orthodontists should refer patients to appropriate healthcare providers for further evaluation and treatment.
– Customized Treatment Plans: For patients with known eating disorders, orthodontists may need to adjust their treatment plans to accommodate their specific needs. For instance, the use of removable appliances like clear aligners may be more appropriate for some patients, as they can be taken out during episodes of vomiting to prevent acid exposure to the teeth. In cases of bruxism, orthodontists might recommend additional appliances, such as mouthguards, to protect the teeth during sleep.
– Focus on Oral Hygiene Education: Educating patients about proper oral hygiene is vital for preventing complications during orthodontic treatment. This is especially important for individuals with eating disorders, who may be at an increased risk for tooth decay, gum disease, and enamel erosion. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings should be emphasized, along with personalized oral hygiene instructions that take into account the presence of orthodontic appliances.
– Nutritional Support: Orthodontic care for patients with eating disorders should also involve nutritional counseling to ensure that they are receiving the vitamins and minerals necessary for optimal oral health. Adequate calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients can help strengthen teeth and gums, supporting orthodontic treatment and improving overall health.
4. Long-term Considerations for Optimal Oral Health
Achieving optimal oral health in patients with eating disorders is not only about the success of the orthodontic treatment itself but also about long-term maintenance. After the completion of orthodontic care, patients must be committed to regular dental check-ups, maintaining good oral hygiene, and continuing any necessary nutritional or psychological therapy.
It is important to recognize that eating disorders often require long-term management, and orthodontic care is just one component of the broader approach to the patient’s overall health. Orthodontists should remain vigilant in monitoring their patients for any signs of relapse or oral health issues post-treatment.
Orthodontic treatment can be a challenging process for individuals with eating disorders, but with careful management and collaboration, it is possible to achieve optimal oral health. By understanding the complexities of how eating disorders affect oral health and orthodontic care, dental professionals can provide more effective treatment plans and ensure better long-term outcomes for their patients.
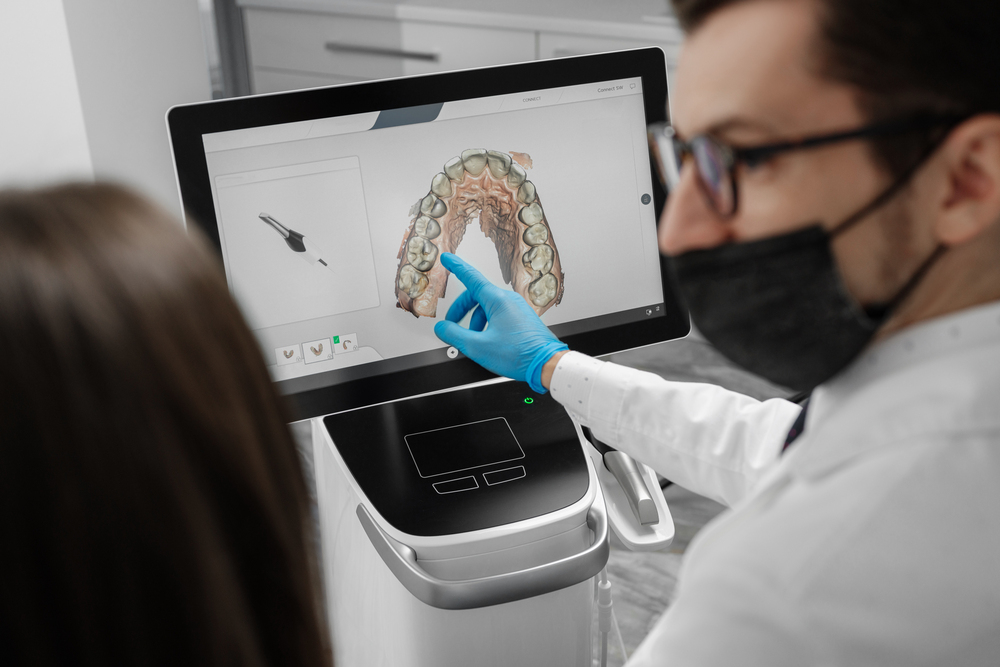
The Future of Orthodontics: How AI-Driven Treatment Plans Are Enhancing Precision
Orthodontics has come a long way from its early days of metal wires, brackets, and uncomfortable headgear. In the past few decades, technology has accelerated the field of dentistry, especially in orthodontics, where traditional methods are being enhanced or even replaced by cutting-edge tools. One of the most transformative advancements is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into orthodontic treatment planning. By using AI to analyze data and generate highly personalized treatment plans, orthodontists are improving the precision and efficiency of care, reducing treatment times, and enhancing overall patient outcomes.
The Role of AI in Orthodontics
AI is revolutionizing the way orthodontists approach diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up care. With AI-powered software, orthodontists now have access to tools that can analyze vast amounts of data, including digital scans, X-rays, and patient history, to develop a highly customized treatment plan. These AI systems learn from thousands of cases and continuously improve, allowing them to make highly accurate predictions about how a patient’s teeth will move during treatment.
AI-driven orthodontics focuses on two key aspects: precision and efficiency. The technology eliminates much of the trial and error that was previously common in traditional treatment plans, enabling orthodontists to achieve more predictable outcomes. With the ability to analyze 3D models of a patient’s teeth, AI systems can predict how teeth will move over time and what the final result will look like—something that was once impossible without extensive experience and manual calculation.
Enhancing Precision with AI
One of the primary benefits of AI in orthodontics is its ability to enhance precision at every stage of the treatment process. Traditional orthodontics relied heavily on manual measurements and physical models, which left room for human error. AI, on the other hand, can process thousands of data points simultaneously, allowing for an incredibly detailed analysis of the patient’s dental structure. This leads to a higher degree of accuracy in diagnosing malocclusions and planning the movement of teeth.
AI software can create 3D digital models from scans of the patient’s mouth, identifying the most efficient way to move each tooth to its optimal position. This type of analysis is crucial for reducing treatment time and ensuring that each tooth moves exactly where it needs to go, without unnecessary adjustments.
Moreover, AI systems continuously learn from data—meaning that with every patient, the technology becomes even more effective. By incorporating feedback loops, these systems can adapt and refine treatment plans mid-treatment, ensuring that any deviations from the predicted outcome are corrected in real time. This adaptability is a significant improvement over traditional methods, where mid-treatment adjustments often required time-consuming manual intervention.
AI-Powered Clear Aligners
Clear aligners, such as Invisalign, have been one of the most popular orthodontic advancements in recent years, and AI has played a significant role in their success. Aligners work by gradually shifting teeth into the desired position, and each aligner is slightly different from the last. Designing these aligners requires careful planning, and AI algorithms have significantly improved this process.
AI is now being used to optimize the design of clear aligners, predicting the best sequence of movements for each tooth. With AI-driven simulations, orthodontists can visualize the entire treatment plan, from start to finish, before the patient even begins wearing their first aligner. This level of precision minimizes the risk of complications and reduces the number of adjustments that are needed throughout the course of treatment.
For patients, this means a more comfortable and predictable treatment experience. They can achieve their desired results in less time, often with fewer in-office visits. Additionally, many clear aligner companies now offer remote monitoring options, where AI tools can track the patient’s progress using smartphone photos or at-home scanning devices. This reduces the need for frequent check-ups while ensuring that the treatment is on track.
Accelerating Treatment Times
Traditional orthodontic treatments could take anywhere from 18 months to three years, depending on the severity of the case. However, AI is helping to reduce this timeline significantly. AI’s ability to predict how teeth will move allows orthodontists to plan treatment more effectively, optimizing the sequence of tooth movements to reduce overall treatment time. This is particularly beneficial for adult patients, who are often seeking quicker, more discreet solutions to orthodontic issues.
In addition to reducing treatment time, AI also helps prevent unnecessary delays caused by human error or miscalculations. With AI-driven tools handling the planning and monitoring of treatment, orthodontists can focus more on patient care and less on manual adjustments, which helps streamline the entire process.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Orthodontic treatment is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and each patient’s mouth is unique. AI-driven systems are able to account for this individuality by creating personalized treatment plans tailored to the specific needs of each patient. The software can analyze multiple factors, including the patient’s dental history, the shape and size of their teeth, and their bite alignment, to develop a customized treatment plan.
This level of personalization extends to predicting how the patient’s teeth will respond to different treatment options. By simulating various scenarios, AI can help orthodontists decide whether traditional braces, clear aligners, or another method will be the most effective for a given patient. These insights help orthodontists make more informed decisions, leading to better patient outcomes.
The Future of AI in Orthodontics
As AI technology continues to evolve, its role in orthodontics will only grow. We can expect AI-driven tools to become even more sophisticated, offering more precise and efficient treatment options. In the future, AI may play a key role in fully automating parts of the orthodontic workflow, from initial diagnosis to the design and fabrication of custom appliances.
Moreover, AI could integrate with other emerging technologies, such as robotics and augmented reality, to further enhance treatment accuracy and patient experience. For example, robotic systems could apply forces with unparalleled precision, while augmented reality might allow patients to visualize their post-treatment smiles in real time.
AI-driven treatment plans are revolutionizing the field of orthodontics, offering enhanced precision, shorter treatment times, and personalized care. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will play an even more significant role in shaping the future of orthodontic care, improving outcomes for both patients and practitioners. For orthodontists, embracing AI is no longer just an option—it is the key to staying at the forefront of this rapidly advancing field.

Pediatric Dental Care: When Should You Start and What to Expect
The importance of pediatric dental care cannot be overstated. In order for your child to have a healthy smile it starts before their first set of teeth erupt. Knowing when to begin and how to get started on caring for your child’s teeth is important to help keep your child’s mouth healthy for now and for the long term. In this article, we will explore the key timelines for pediatric dental care, the benefits of starting early, and how to address common dental problems in children.
Orthodontics in Australia: Embracing the Highest Standards of Technology & Care
Orthodontics, the dental specialty concerned with diagnosing, preventing, and correcting malpositioned teeth and jaws, has evolved dramatically in recent years. Australia, known for its high standards of healthcare, stands at the forefront of these advancements. In orthodontics, Australia combines cutting-edge technology with unparalleled patient care, offering innovative solutions for achieving functional, aesthetically pleasing smiles. This article explores the advancements, trends, and the overall approach to orthodontic care in Australia that have made it a leader in the field.
The Evolution of Orthodontics
Orthodontics in Australia has evolved from traditional metal braces to a broad spectrum of options designed to cater to diverse patient needs. In the past, orthodontic treatment was often associated with long, uncomfortable processes dominated by unsightly metal braces. Today, patients have access to advanced techniques that improve comfort, reduce treatment duration, and enhance cosmetic outcomes. These advancements are largely due to Australia’s commitment to adopting new technologies and maintaining stringent standards for training and certification.
The Australian Society of Orthodontists (ASO) plays a pivotal role in ensuring the highest level of care. Only dentists who undergo an additional three years of postgraduate training can register as certified orthodontists. This rigorous training ensures that Australian orthodontists are equipped with the expertise needed to diagnose complex dental issues and provide tailored treatment plans using state-of-the-art technology.
Cutting-Edge Technology in Australian Orthodontics
1. Digital Orthodontics and 3D Imaging
One of the most transformative technologies in orthodontics is the use of digital orthodontics, which includes 3D imaging, digital scans, and computer-aided design. Traditional orthodontics relied on physical molds and x-rays, which were less precise and often uncomfortable for patients. In contrast, modern orthodontics in Australia embraces digital scanning technology which captures detailed images of the patient’s teeth and jaws without the need for messy impression molds.
3D imaging technologies such as cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) allow orthodontists to create highly accurate models of the mouth, teeth, and jaw structures. This enables precise treatment planning, reducing the chance of errors and enhancing the predictability of outcomes. Orthodontists can simulate the movement of teeth over time, giving patients a clear picture of their expected results before treatment even begins. This level of precision is particularly beneficial for complex cases, such as patients with severe misalignments or those requiring surgical interventions.
2. Clear Aligners: Invisalign and Beyond
One of the most popular advancements in orthodontic treatment is the rise of clear aligners. Invisalign, the market leader in this category, has revolutionised the way patients perceive orthodontic care. Unlike traditional braces, which rely on metal brackets and wires, clear aligners use custom-made, transparent trays to gradually move teeth into alignment. These aligners are virtually invisible, offering an aesthetic solution for adults and teenagers who may feel self-conscious about traditional braces.
Clear aligners also offer practical benefits, such as the ability to remove them for eating and cleaning, which improves oral hygiene during treatment. Australia has embraced this technology wholeheartedly, with many orthodontists offering not only Invisalign but also other clear aligner options. The increasing availability of clear aligners has broadened access to orthodontic care, providing more flexibility and convenience for patients.
3. Self-Ligating Braces
Though traditional braces remain a reliable method for orthodontic treatment, advancements have been made in their design. Self-ligating braces are an innovative alternative to conventional metal braces. These braces use a special clip or sliding mechanism to hold the wire in place, eliminating the need for elastic bands. This system reduces friction and pressure on the teeth, making the process more comfortable for patients.
Self-ligating braces also allow for faster tooth movement, which can shorten treatment times. Additionally, they are easier to clean and maintain, reducing the risk of plaque buildup and gum disease. Many orthodontists in Australia now offer self-ligating braces as an option, particularly for patients seeking a balance between effectiveness and comfort.
4. Lingual Braces
For patients who want the reliability of traditional braces but prefer a discreet option, lingual braces provide a solution. Lingual braces are placed on the inside surface of the teeth, making them virtually invisible from the outside. Although they function similarly to traditional braces, their hidden placement makes them an attractive choice for patients concerned about aesthetics.
While lingual braces require specialised training to apply, many Australian orthodontists have mastered this technique. Lingual braces are ideal for patients who want an inconspicuous treatment option without compromising on effectiveness. As orthodontists continue to refine their skills with lingual braces, they are becoming an increasingly popular choice in Australia.
Patient-Centered Care: Personalising Orthodontic Treatment
Australia’s orthodontic practices emphasise personalised care, ensuring that each patient receives a tailored treatment plan based on their unique dental needs. Orthodontists in Australia take the time to thoroughly assess each case, considering factors such as age, oral health, and personal preferences when designing a treatment plan.
Patient education is also a key component of care. Orthodontists in Australia ensure that patients understand their treatment options, the expected duration of care, and the potential outcomes. This patient-centered approach builds trust and helps patients feel more confident and informed about their treatment journey.
Additionally, Australian orthodontists are known for their focus on patient comfort. From offering pain management solutions to providing flexible payment plans, orthodontic practices in Australia strive to make treatment as accessible and stress-free as possible. Many clinics also offer virtual consultations, allowing patients to receive advice and assessments remotely, which is particularly valuable in rural areas or for patients with busy schedules.
The Role of Preventative and Early Intervention Orthodontics
In line with global trends, Australian orthodontists have increasingly adopted preventative and early intervention strategies. By identifying and addressing potential orthodontic issues in children as young as seven, orthodontists can guide jaw growth and prevent more severe problems from developing later in life. This proactive approach can reduce the need for more invasive treatments down the line, such as tooth extractions or jaw surgery.
Orthodontists in Australia work closely with pediatric dentists to monitor the development of children’s teeth and jaws. Early intervention often involves using expanders, space maintainers, or partial braces to correct issues as they arise, promoting healthier oral development.
The Future of Orthodontics in Australia
As technology continues to evolve, the future of orthodontics in Australia looks promising. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are expected to play a role in further improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. AI-driven software can analyze data from thousands of cases to recommend the most effective treatment paths, potentially leading to even shorter treatment times and better outcomes.
Moreover, innovations such as 3D-printed aligners and smart braces equipped with sensors to monitor treatment progress in real-time are on the horizon. These technologies, coupled with Australia’s commitment to high-quality care, will ensure that orthodontics in the country remains at the cutting edge of global practices.
Australian Orthodontists Leading The World
Orthodontics in Australia is defined by its adoption of the latest technologies, a patient-centered approach, and a commitment to providing the highest standards of care. From digital orthodontics and clear aligners to early intervention strategies, Australian orthodontists offer a comprehensive array of treatment options that prioritise both aesthetics and function. As the field continues to advance, patients can expect even more efficient, comfortable, and personalized care, solidifying Australia’s position as a leader in orthodontic innovation.
The Role of Orthodontics in Modern Dentistry: Improving Function and Aesthetics
Orthodontics, once primarily associated with metal braces for adolescents, has evolved significantly in the realm of modern dentistry. Today, orthodontics plays a crucial role not only in enhancing the aesthetic appeal of smiles but also in improving overall oral function and health. As dentistry continues to grow, orthodontics has seen remarkable advancements in techniques and technologies, making it an integral part of comprehensive dental care.
Aesthetic and Functional Benefits of Orthodontics
Orthodontics focuses on diagnosing, preventing, and treating dental and facial irregularities. Misaligned teeth, overcrowded mouths, overbites, underbites, and jaw misalignments are common issues addressed through orthodontic treatment. These treatments go beyond the surface of merely straightening teeth; they profoundly impact both aesthetics and function.
From an aesthetic perspective, a well-aligned smile boosts self-esteem and confidence. A beautiful smile is often one of the first features people notice, and it significantly influences personal and professional interactions. However, the benefits of orthodontics extend far beyond appearance. Properly aligned teeth are easier to clean and maintain, reducing the risk of cavities, gum disease, and other oral health problems. Furthermore, orthodontic treatment can correct bite issues that, if left untreated, may lead to excessive wear on teeth, jaw pain, and even speech difficulties.
Technological Advancements Driving Growth in Orthodontics
The growth in dentistry, particularly within orthodontics, is largely driven by technological advancements that have transformed patient experiences and outcomes. Traditional metal braces, once the hallmark of orthodontic care, have been supplemented—and in some cases replaced—by innovative alternatives like clear aligners, lingual braces, and self-ligating braces.
Clear aligners, such as Invisalign, have revolutionized orthodontic treatment by offering a discreet and comfortable option for patients. These aligners are nearly invisible, removable, and custom-made for each patient, providing a more convenient and aesthetically pleasing alternative to traditional braces. Clear aligners are especially popular among adults who seek orthodontic treatment without the noticeable appearance of metal braces.
Lingual braces, which are placed on the back of the teeth, offer another discreet option for patients who need more comprehensive corrections than clear aligners can provide. Meanwhile, self-ligating braces use a specialized clip instead of elastic bands, reducing friction and often shortening the treatment time.
These advancements reflect the broader growth in dentistry as it increasingly embraces digital technology. Digital scanning and 3D imaging allow orthodontists to create precise treatment plans, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of care. The ability to visualize the expected outcome of treatment before it begins helps patients understand their journey and fosters greater confidence in the process.
Orthodontics for All Ages: Expanding Access and Appeal
Historically, orthodontic treatment was often viewed as a rite of passage for teenagers. However, with the growth in dentistry, orthodontics has become accessible and appealing to patients of all ages. Adults now make up a significant portion of orthodontic patients, driven by the desire to improve their smiles and oral health later in life.
The increasing availability of less invasive and more aesthetically pleasing treatment options has fueled this trend. Adult orthodontics not only addresses aesthetic concerns but also improves function, which can lead to better long-term oral health outcomes. For example, correcting malocclusion (improper bites) can alleviate chronic jaw pain and prevent future dental issues that might arise from abnormal wear and tear on teeth.
Additionally, early intervention in children—sometimes referred to as interceptive orthodontics—aims to guide the growth of the jaw and incoming teeth. By addressing issues early, orthodontists can often reduce the need for more extensive treatment later. This proactive approach underscores the expanding role of orthodontics in modern dentistry, emphasizing prevention and early correction.
The Future of Orthodontics: Personalization and Patient-Centered Care
As orthodontics continues to grow within the field of dentistry, the focus is shifting increasingly toward personalization and patient-centered care. Orthodontic treatments are no longer one-size-fits-all; they are tailored to meet the specific needs and goals of each patient. Advances in technology, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are paving the way for even more precise and efficient treatment planning.
Orthodontists are now able to offer more customized solutions, predicting tooth movements and treatment outcomes with greater accuracy than ever before. This growth in dentistry not only improves the patient experience but also enhances the overall effectiveness of treatments.
Furthermore, patient education and engagement are becoming more central to orthodontic care. By involving patients in their treatment planning and providing clear explanations of the benefits and expectations, orthodontists can improve patient satisfaction and compliance.
Orthodontics has transformed from a niche branch of dentistry focused primarily on aesthetics to a critical component of comprehensive oral health care. With advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on personalization, orthodontics plays a vital role in modern dentistry, enhancing both function and aesthetics. As the field continues to grow, orthodontic treatments will likely become even more accessible, efficient, and tailored to individual needs, helping patients of all ages achieve healthier, more beautiful smiles. The ongoing evolution of orthodontics within the broader context of dentistry underscores its importance in improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
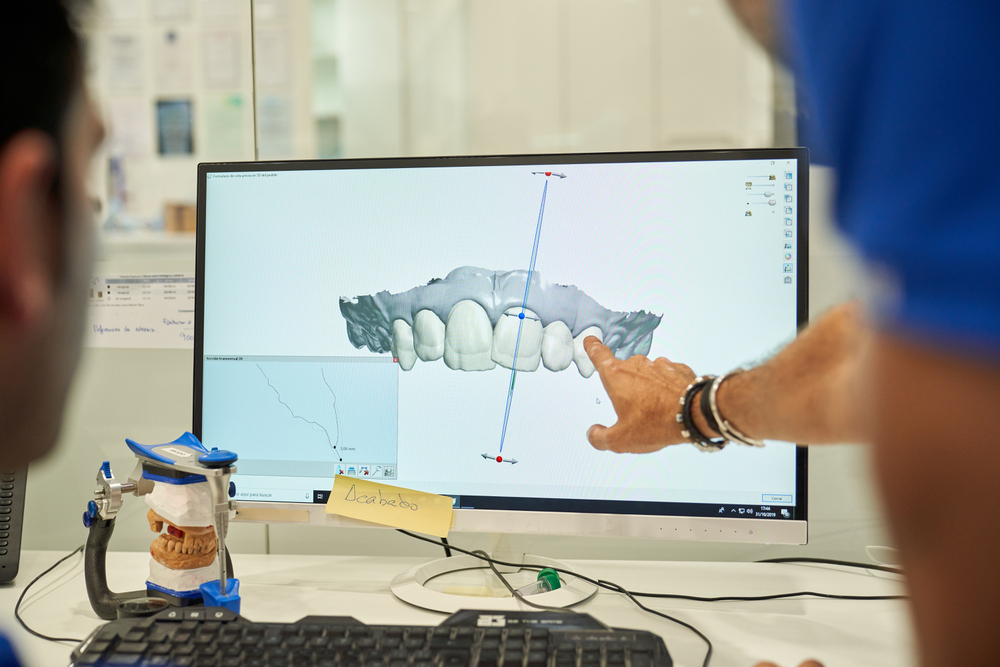

From Vision to Reality: How Digital Smile Design Transforms Cosmetic Dentistry
Are you familiar with digital smile design? It is the latest technology that is improving the cosmetic dentistry segment significantly. The use of this technology is helping doctors to get more precise results. In this blog, we will talk about the basics of digital smile design, the impacts it has, and some more.
Both patients and doctors are benefitting from it. Right now, many dentists are using this innovation to visualize dental treatment and procedures. If you can plan better, it means you will have better results too. Popular dental clinics are now offering state-of-the-art services like digital smile design and more. Keep reading so that you can understand better about these things.
Basics You Need to Know About Digital Smile Design
For those who don’t know, digital smile design is nothing but advanced software. Professionals are using this software to have a mock-up smile design that the patient is going to have after the treatment.
As you are getting the view from advance, it is helping people to plan everything and make changes if needed. Every one of us has a different facial structure; now, you can check whether a particular type of smile is good for you or not.
Aspects That Are Important to Know
- Before going through the implant, it is important to learn some of the following aspects:
- Digital smile design platforms can get you an exact representation before the surgery. Once you are happy with the results, then only the professionals will start working on that.
- Smile design is helpful in making customized smiles as per human anatomy, dental position and other aspects.
- With time, we are getting precise results. In the coming years, we are going to have further results.
Long-Term Impacts We Are Going to Face
- In most cases, the patients are happy with the results they are getting.
- Use of this process has reduced anxiety and other mental issues significantly.
- The process is giving us consistent results.
Key Elements of Digital Smile Design
After talking to experts, we have come up with the following elements regarding digital smile design. People are implementing a business acceleration strategy based on this treatment procedure.
Consultation Process
The first thing that you need to do is go to a dental expert and consult with him. There, you will learn about how photographs, 3D scans, and videos will impact the process. In the later part, experts will use these items and advanced software to predict future outcomes.
What About Simulation?
After careful analysis, digital simulation will create a perfect smile best suited for your face. You can see the preview and decide whether you want that result or not. Only after your nod, the experts will start the actual process.
How to Plan Your Treatment?
In the planning part, doctors will run through all the small details like choosing the veneers, crowns, and other items. You will have every little information so that you don’t feel much uncomfortable during the process.
Execution Process
When the planning is near perfect, you don’t need to worry much about the execution part. Modern dentists are trained to carry out any dental process and ensure accurate results.
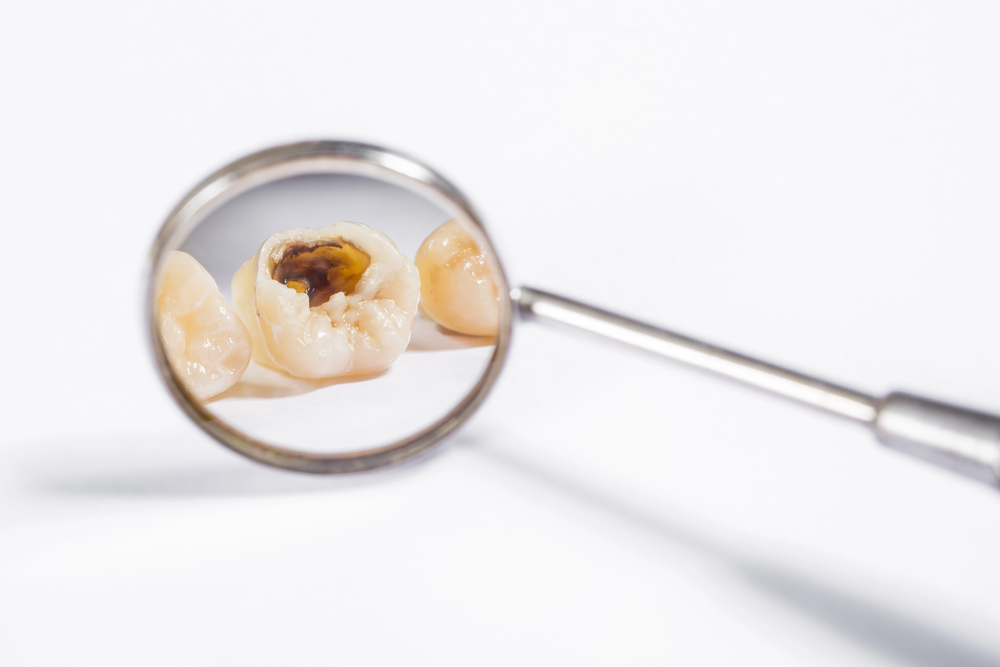
The Facts, Fundamentals, and Fallacies of Tooth Decay Worth Knowing
Tooth decay is a common challenge in dentistry and is caused by dental cavities. About 80% of adults suffer from dental holes. The decay emanates from bacteria that stick to our teeth and feed on the sugars and food that make acids in our mouths. The acid eventually wears out the tooth enamel and causes a cavity. While most people understand tooth decay, their judgment is crowded by some myths that prevent them from accessing sufficient dental care. Here are essential facts about tooth cavities and fallacies to avoid while dealing with tooth decay.
Fundamental Facts about Tooth Decay
Tooth decay does not always show symptoms. It is true that you can have tooth decay and fail to show any signs. It is therefore important to visit dentist on regular basis. While it is possible not to identify the signs, a dentist will recognize them through examination and guide you on the best treatment methods. The best thing is that, with the correct diagnoses, modern dentists can offer a range of services to help eliminate tooth decay.
An ignored cavity does not stop growing until addressed. It develops through all your teeth layers up to a point where you can no longer ignore it due to the excruciating pain. When you ignore the cavity for long, it becomes expensive to treat it. A simple filing can eliminate a cavity but ignoring it can lead to extraction or the need for a root canal.
Sugar is one of the largest causes of tooth decay. Consuming foods that contain excessive sugar, such as, candies, bread, fruits, and sweets increases cavities. These foods work with the bacteria in your mouth to form acid, eventually destroying your teeth.
Statistics and data on oral health around the world suggest that tooth cavities lead to tooth loss when not treated on time. At the initial stages, decay seems harmless but can damage your tooth structure. It causes the tooth to break, thus, requiring extraction to avoid infecting the other teeth.
Fallacies about Tooth Cavities
Brushing alone prevents tooth decay. This is a belief that most people tend to follow. Tooth brushing is important but cannot prevent decay all alone. You should always floss after brushing to eliminate the remaining bacteria in your mouth.
Cavities are only for children. They can occur at any stage of life if you do not care for your teeth well. Dry mouth increases the chances of cavities, a common issue in adults using chronic medications. Genetic predispositions and prolonged consumption of sugary products also cause cavities.
When teeth are not hurting, there is no problem. You might have tooth decay and yet no pain. A tooth hurts when the damage is beyond control, and thus, we should always go for checkups to identify and eliminate tooth decay before it becomes too serious.
In conclusion, tooth decay is a serious issue that affects people of all ages. It is important to understand tooth decay, how to identify it, and the methods to deal with it. Avoid believing in all the fallacies people spread about tooth cavities and focus on understanding the facts. Visit the dentist regularly and read materials about tooth cavities to be informed about the correct ways to prevent them.
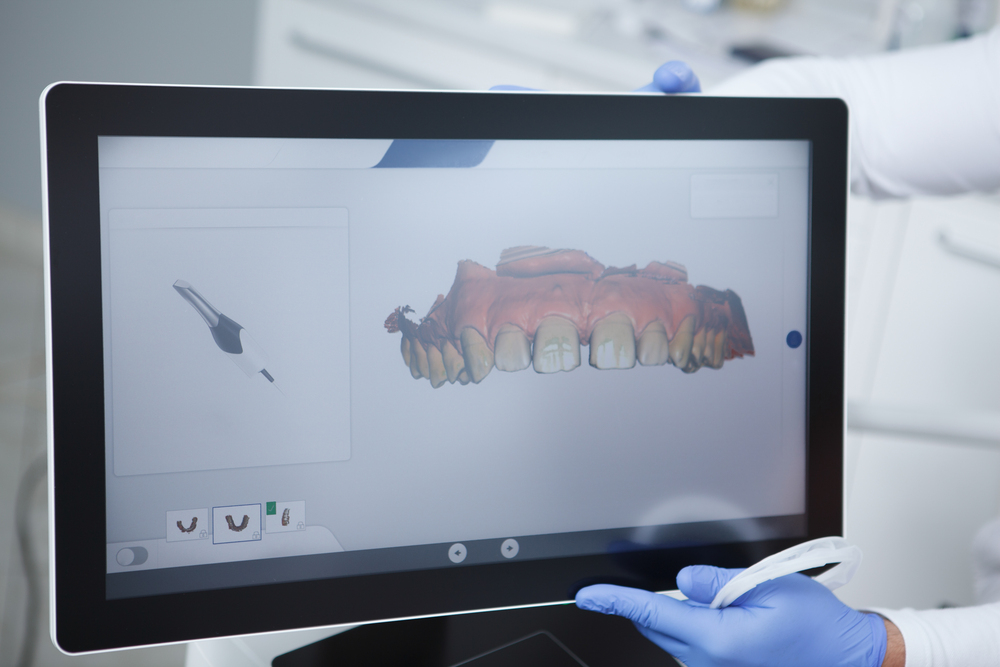

How Innovative Has Cosmetic Dentistry Become?
A smile creates a person’s first impression, and having a beautiful smile appears to be an advantage in life, careers, and of course in relationships and marriage. However, some people have teeth which are not properly aligned, preventing them from having a confident smile. Recently, cosmetic dentistry has improved and changed people’s smiles. This article will focus on technological advancements and innovations that enable dentists to help patients achieve their dream smile. Here are several innovations in cosmetic dentistry.
Intraoral Cameras
The frame of your teeth structure is vital in transforming your teeth arrangement, and the dentist is required to view it properly for better treatment. An intraoral camera provides dentists with an internal picture of the patient’s mouth. These pictures are used to enable the dentist to gain a better idea of your tooth structure and identify the correct method to rectify them. The intraoral camera is flexible, allowing it to reliably examine all distortions at any corner of the tooth.
Digital Smile Design (DSD)
DSD has become vital in cosmetic dentistry by enabling meticulous planning to achieve a good smile. The latest advancement of DSD incorporates software and imaging technologies that allow visualization of the face, tooth proportion, and lip appearance to ensure a natural and harmonious look. It enables you to have a glimpse of how you will look even before the treatment begins. The technique enables individuals to choose the best option that meets their expectations. For these reasons, many people seek out a cosmetic dentist to correct imperfections and improve the appearance of their smile by starting at the digital design stage.
Teeth Whitening
Tooth whitening is more affordable and refined due to technological advancements such as laser-assisted and modified whitening measures. People can now smile confidently, thanks to teeth whitening methods of bleaching teeth. The innovations have reduced the treatment time and increased the overall outcomes.
3D Printing
It is used in creating custom-made crowns, aligners, and dentures. The advancements of 3D printing has improved cosmetic dentistry treatment and personalized dental prostheses. Dentists can now create bridges and crowns with the help of the technology at their comfort. The use of an intraoral camera helps in digitally capturing teeth impressions and eliminates the use of traditional stressful impression materials. The technology has enhanced accuracy, simplified dentistry work, and improved patients’ experience.
Minimally Invasive Veneers
Veneers have been used to improve people’s smile for a long time. Today’s innovations make the technique more appealing and suitable as patients can improve their smile without altering with their tooth structure. The advanced veneer materials help dentists offer transformative results with less discomfort. The technology offers a patient the advantage of retaining their natural tooth structure while achieving the desired aesthetic.
Tele-Dentistry
It is an online service through which patients can access dental care remotely through virtual consultations. The dentist arranges for online sessions with their patients, reducing the time required to visit the office. The dentist can even guide the patients on how to get the best dentistry books on the market and read them to gain more knowledge about their teeth while they are at home.
The bottom line is that technological innovations have significantly improved cosmetic dentistry. People can now achieve their dream smile with the snap of a finger. Recent methods enable dentists to deliver satisfying results to their patients with less time and less discomfort. Dentists have changed the way they approach aesthetic treatments and improved patient experience. The innovations have transformed dental care and paved the way for more efficient and patient-centric approaches.
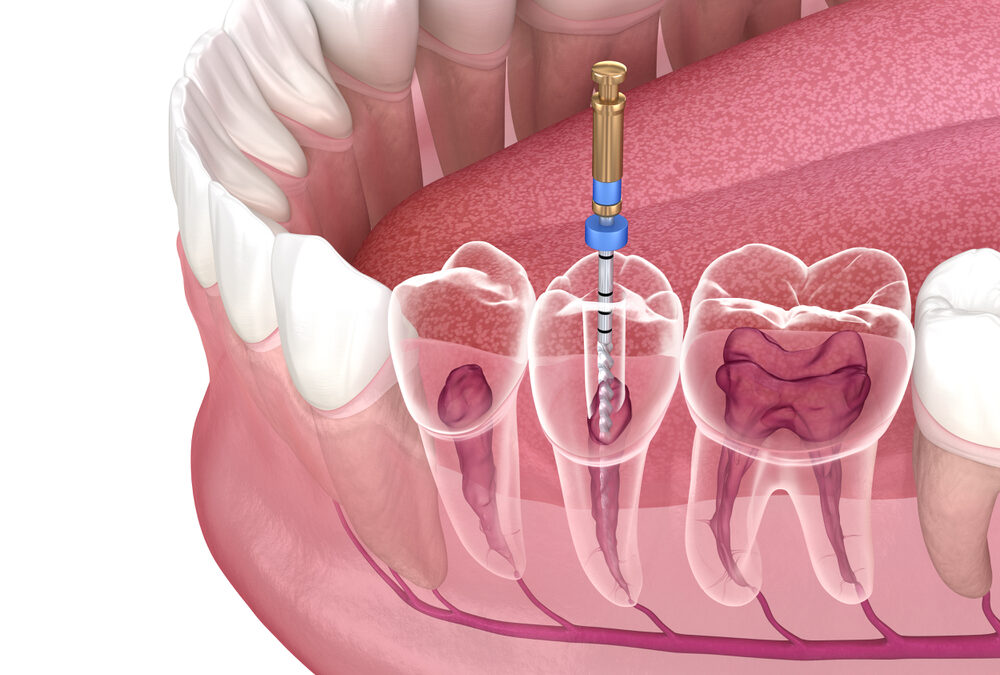
Root Canals Explained: What Happens to Your Tooth Nerve and Why It Matters
When it includes dental fitness, few strategies are as substantially stated—and every so often misunderstood—as a root canal. Often related to worry and pain, root canal treatment is, in fact, a not unusual and powerful manner designed to keep a teeth that could otherwise want to be extracted. But what exactly takes area for the duration of a root canal, and why is it so crucial for the health of your teeth? Understanding the area of your enamel nerve in this technique can help demystify the method and underscore its significance.
The Anatomy of a Tooth
To hold close to the importance of a root canal, it’s essential to first apprehend the form of a tooth. Each enamel consists of numerous layers:
1. Enamel: The difficult, outer layer that protects the teeth.
2. Dentin: The layer below the enamel, that is tons much less dense but although quite hard.
3. Pulp: The innermost a part of the enamel, containing the nerve and blood vessels.
The pulp, often called the enamel nerve, is crucial for the teeth’s health and sensation. It elements vitamins and is answerable for the teeth’s response to temperature changes and awesome stimuli. However, if the pulp will become damaged or infected, it is able to bring about immoderate pain and probable threaten the survival of the teeth.
What Is a Root Canal?
A root canal is a dental technique designed to cope with problems inside the pulp of a teeth. When the pulp becomes infected or inflamed due to decay, trauma, or exclusive problems, it may motive sizable ache and headaches. Root canal treatment desires to put off the damaged pulp, clean the internal of the enamel, and seal it to prevent future infections.
Here’s a step-via-step examine of the system:
1. Diagnosis: The dentist examines the enamel and can use X-rays to evaluate the quantity of the harm or contamination.
2. Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is run to numb the affected region, ensuring the affected man or woman is snug in the course of the gadget.
3. Access Opening: The dentist drills a small hollow within the teeth to get right of entry to the pulp chamber.
4. Cleaning and Shaping: The dentist gets rid of the infected or broken pulp tissue, cleans the muse canals, and shapes them to put together for filling.
5. Filling: The wiped easy canals are entire of a biocompatible material to seal them and prevent destiny infections.
6. Restoration: A transient or everlasting crown is positioned on the enamel to repair its feature and look.
Why the Tooth Nerve Matters
The teeth nerve, or pulp, performs a crucial feature in a teeth’s health. When it will become inflamed, the following pain and sensitivity are frequently excessive, making it easy that there’s a extreme hassle that dreams addressing. The infection can unfold to surrounding tissues, critical to greater important issues, consisting of abscesses or bone loss.
Root canal remedy is essential as it addresses the infection at its deliver, relieving ache and stopping the need for enamel extraction. By preserving the enamel, sufferers preserve their natural chunk and chewing feature, which may be appreciably impacted with the beneficial aid of enamel loss.
Becoming a Dentist: The Path to Performing Root Canals
For those interested in pursuing a career in dentistry, becoming proficient in procedures like root canal treatment is essential. A dentist must complete extensive education and training, including:
1. Undergraduate Education: A bachelor’s diploma in a applicable place, at the aspect of biology or chemistry, is commonly required.
2. Dental School: Attending an authorized dental university is vital for studying the abilities important to carry out numerous dental techniques, which includes root canals.
3. Licensing: Dentists want to bypass countrywide and u . S . Licensing tests to exercise professionally.
4. Postgraduate Training: Some dentists pick out out to specialize further, with greater training in endodontics (the branch of dentistry focusing on root canal treatment).
For aspiring dentists, mastering root canal remedy is virtually one detail of a huge talents set required for a a hit profession. The capability to diagnose, deal with, and manipulate numerous dental situations is important for offering exquisite care to patients.
The Importance of Early Intervention
One of the keys to a success root canal treatment is early intervention. If you revel in symptoms and symptoms which includes chronic toothache, extended sensitivity to heat or bloodless, or swelling throughout the gums, it’s critical to peer a dentist as fast as feasible. Early evaluation and remedy can save you more splendid damage and boom the possibility of a a success outcome.
The Takeaway
Root canal treatment is a important method in contemporary dentistry, presenting a way to preserve a teeth that could in any other case be out of place due to contamination or harm. Understanding what takes place for your enamel nerve at a few stage inside the method can assist alleviate fears and spotlight the significance of well timed intervention. For the ones interested in becoming a dentist, gaining knowledge of strategies like root canals is a key hassle of the schooling and skills required to deliver effective dental care.
By appreciating the position of root canal remedy and the enamel nerve, sufferers and future dentists alike can better understand the rate of this essential dental technique.
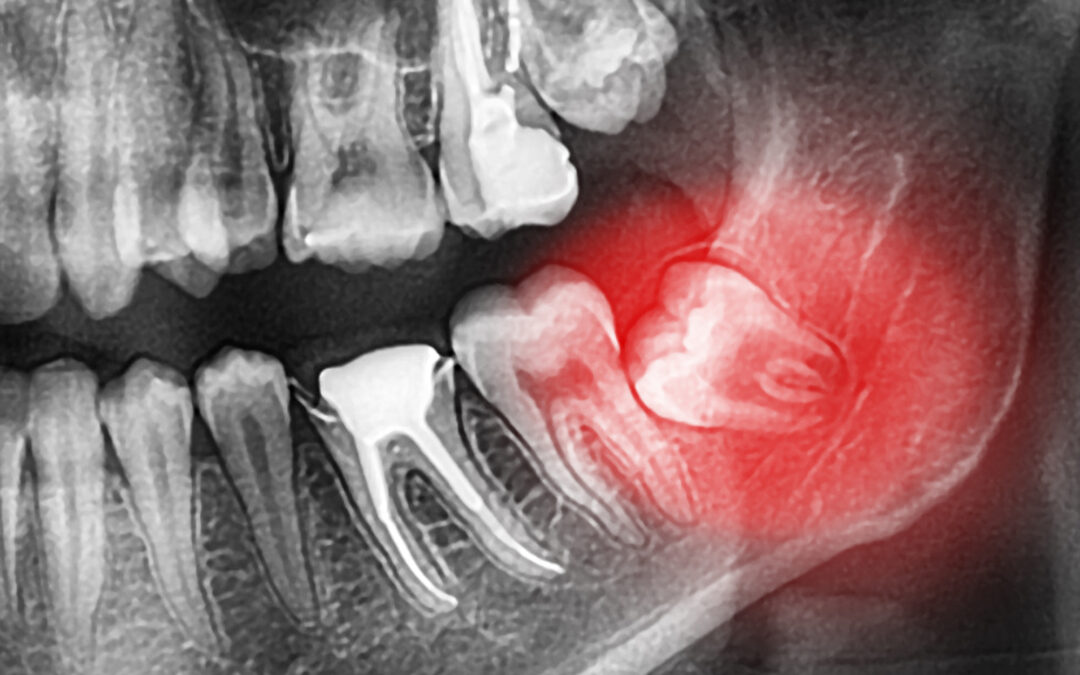
Wisdom Teeth Removal: How It Can Benefit Your Long-Term Health
Wisdom teeth, the third set of molars located at the back of your mouth, often become a topic of concern as they begin to emerge during late adolescence or early adulthood. For many, these teeth can cause more trouble than they’re worth, leading to the need for wisdom tooth extraction. This common dental procedure is not just about alleviating immediate discomfort but also plays a crucial role in ensuring long-term health benefits. In this article, we’ll explore how wisdom tooth extraction can positively impact your overall health and address common concerns such as dental anxiety.
The Importance of Wisdom Teeth Removal
Wisdom teeth are notorious for causing a range of issues. They often emerge improperly or become impacted, meaning they don’t fully erupt through the gum line. This can lead to a host of problems including:
– Crowding and Misalignment: As wisdom teeth attempt to come in, they can push against neighboring teeth, causing them to shift and potentially disrupt your bite. This misalignment can complicate oral hygiene and may necessitate additional orthodontic treatment.
– Infection and Decay: Partially erupted wisdom teeth create pockets between the tooth and the gum where bacteria can accumulate, leading to infections like pericoronitis. These infections can be painful and may spread if not treated promptly.
– Cysts and Tumors: Impacted wisdom teeth can form cysts or tumors in the jawbone, which may cause bone damage and necessitate further surgical intervention.
By opting for wisdom tooth extraction, you can avoid these potential complications and safeguard your dental health. But the benefits extend beyond just avoiding immediate dental issues.
Long-Term Health Benefits of Wisdom Tooth Extraction
1. Reduced Risk of Oral Health Complications: By removing wisdom teeth before they cause significant problems, you can avoid chronic issues such as gum disease, decay, and infections. This proactive approach helps maintain your oral health and reduces the need for more invasive treatments in the future.
2. Preventing Tooth Misalignment: As mentioned, wisdom teeth can crowd or shift other teeth, potentially undoing years of orthodontic work. By extracting them early, you can help preserve the alignment of your teeth and avoid the need for additional orthodontic correction.
3. Enhanced Overall Health: Oral infections and diseases can have far-reaching effects on your overall health. For example, untreated gum disease is linked to conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues. By ensuring that wisdom teeth are properly managed, you can minimize the risk of these systemic health problems.
4. Improved Comfort and Quality of Life: Persistent pain or discomfort from wisdom teeth can affect your daily life, including eating, speaking, and even sleeping. Removing these problematic teeth can lead to a significant improvement in your quality of life, allowing you to enjoy daily activities without the hindrance of dental pain.
Addressing Dental Anxiety
For many people, the idea of undergoing a dental procedure like wisdom tooth extraction can trigger significant dental anxiety. It’s essential to address these concerns to ensure a smooth and stress-free experience.
1. Communication with Your Dentist: Open communication with your dentist about your fears and concerns is crucial. They can provide information about the procedure, explain the steps involved, and discuss pain management options. Understanding what to expect can alleviate some of the anxiety associated with the procedure.
2. Sedation Options: Many dental offices offer sedation options to help patients feel more comfortable during the extraction. These can range from local anesthesia to more advanced options like conscious sedation or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the extraction and your personal comfort levels.
3. Post-Operative Care: Knowing that you have a plan for recovery can also help ease anxiety. Your dentist will provide instructions on how to care for your mouth after the extraction, including tips on managing pain and avoiding complications. Following these guidelines can help ensure a smooth recovery process.
4. Support System: Having a trusted friend or family member accompany you to the appointment can provide additional comfort and support. They can help you navigate the post-operative period and ensure that you follow the care instructions provided by your dentist.
Wisdom tooth extraction may seem like a daunting prospect, but its benefits for long-term health are significant. By addressing potential complications early and managing dental anxiety effectively, you can enjoy better oral health and overall well-being. Removing wisdom teeth not only prevents immediate issues but also helps preserve your dental alignment, reduce the risk of systemic health problems, and improve your quality of life. If you’re experiencing issues with your wisdom teeth or have concerns about the procedure, consult with your dentist to discuss the best course of action for your health.

Hollywood’s Smile Makers: Inside the World of Celebrity Dentists
In the glitzy world of Hollywood, where appearances can make or break a career, having a perfect smile is more than just a matter of dental health—it’s a crucial aspect of personal branding. The architects behind these dazzling smiles are celebrity dentists, experts who have mastered the art of dental aesthetics to cater to the elite. One name that stands out in this illustrious field is Dr. Pabustan of Dental Couture. His expertise, combined with the power of social media, has revolutionized the way we perceive dental care in the entertainment industry.
The Art of Dental Aesthetics
Dental aesthetics is a specialized field that goes beyond routine dental care. It involves a combination of science and art to enhance the appearance of teeth, gums, and overall smile. Celebrity dentists like Dr. Pabustan are not just dental professionals; they are artists who meticulously craft smiles that exude confidence and charisma. Their work involves procedures such as teeth whitening, veneers, crowns, and orthodontics, all tailored to meet the unique needs of their high-profile clients.
Dr. Pabustan of Dental Couture
Dr. Pabustan has become a household name in Hollywood, known for his exceptional skills and innovative approach to dental aesthetics. Based in the upscale clinic, Dental Couture, Dr. Pabustan caters to a clientele that includes A-list actors, musicians, and influencers. His philosophy revolves around providing personalized care, ensuring that each smile he creates is as unique as the individual behind it.
At Dental Couture, the focus is on creating a luxurious experience for patients. The clinic is designed to offer a serene and comfortable environment, equipped with state-of-the-art technology. Dr. Pabustan’s team comprises highly skilled professionals who share his commitment to excellence. Together, they work to transform smiles and boost the confidence of their clients, one appointment at a time.
The Role of Social Media
In today’s digital age, social media plays a pivotal role in the success of celebrity dentists. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube have become powerful tools for showcasing their work and reaching a wider audience. Dr. Pabustan has harnessed the power of social media to build his brand and connect with potential clients.
By sharing before-and-after photos, behind-the-scenes glimpses of dental procedures, and testimonials from satisfied patients, Dr. Pabustan has created a strong online presence. His social media accounts are a testament to his expertise, featuring stunning transformations that highlight his skill and artistry. This transparency not only builds trust with his audience but also educates them about the importance of dental aesthetics.
Moreover, social media allows Dr. Pabustan to stay ahead of trends and innovations in the field. By engaging with followers and fellow professionals, he can exchange ideas and stay updated on the latest techniques and technologies. This continuous learning and adaptation ensure that Dental Couture remains at the forefront of the industry, offering cutting-edge solutions to its clientele.
Transforming Lives, One Smile at a Time
The impact of a beautiful smile extends beyond the superficial. For many celebrities, their smile is a crucial part of their public image and personal brand. A captivating smile can enhance their appeal, boost their confidence, and open doors to new opportunities. Celebrity dentists like Dr. Pabustan understand this dynamic and work tirelessly to help their clients achieve their best smiles.
One of the most rewarding aspects of Dr. Pabustan’s work is witnessing the transformation in his patients’ lives. A radiant smile can significantly improve one’s self-esteem, leading to greater success both professionally and personally. This transformative power of dental aesthetics is what drives Dr. Pabustan and his team to continually strive for excellence.
The Future of Celebrity Dentistry
As the demand for aesthetic dental procedures continues to grow, the field of celebrity dentistry is poised for further innovation and expansion. Advances in technology, such as 3D printing and digital smile design, are revolutionizing the way dentists approach their work. These innovations enable more precise and efficient treatments, resulting in even more stunning and natural-looking smiles.
Additionally, the integration of wellness and holistic approaches into dental care is gaining traction. Celebrity dentists are increasingly focusing on the overall well-being of their patients, considering factors such as nutrition, stress management, and lifestyle choices in their treatment plans. This holistic approach ensures that the results are not only aesthetically pleasing but also sustainable and beneficial for the patient’s overall health.
Hollywood’s smile makers, like Dr. Pabustan of Dental Couture, are more than just dentists—they are artists and innovators who have mastered the delicate balance between science and aesthetics. Through their expertise and the power of social media, they have transformed the field of dental care, making it an integral part of the entertainment industry’s fabric. As they continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, one thing remains certain: the smiles they create will continue to light up the silver screen and inspire confidence in people around the world.
